Month: April 2013
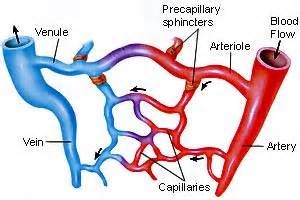
Diagram of capillary bed
Diagram of circulation path
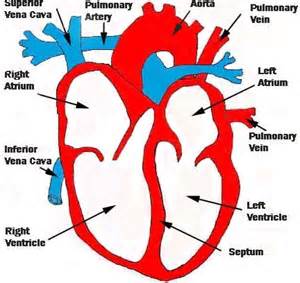
Diagram of heart
9 Joints
| Sport | Ball and Socket | Hinge | Ellipsoidal | Fixed | Gliding | Pivot | Saddle | Slightly Movable | Spine |
| Gangnam Style Dance | -hip, shoulder | – Knees, elbow,
ankles |
– in the wrist, and the bases of the fingers and toes (thumb has different of joint) | – skull | – wrist, ankle, and spine | – neck, elbow | – thumb | – vertebra of the spine | – spine |
Musculoskeleton
-
muscle fiber (more fiber equal more muscle, stronger/bigger muscle)
-
Sarcomeres– repeating units of the muscle fiber
-
consists of 2 types of protein: actin and myosin
-
actin: long thin filaments
-
myosin: ends “in” probably protein. ATP makes the myosin walk on the actin filament (head) as the muscle contract.
-
ATP make the protein change shape.
-
-
Muscle hurts because we are tearing the myosin, and the tears are called microtears (tears of sarcomeres) this is how our muscle get stronger when the muscles rebuilt.
-
2 functions: movement and structure
-
Tendons : muscle attach to bone
-
ligament: bone attach to bone
-
Bone gave us structure
-
Muscle are used for communication, and protection, regulate body temperature (insulation and producing heat)
-
bone marrow: production of red blood cells and white blood cell.
-
Antagonistic pair (muscle) : against each other
-
tongue: attach ton only one bone
-
3 types of muscle: smooth muscle (e.g. Esophagus), cardiac (heart), skeleto
-
Bone: 3 layers (compact bone, spongy bone, marrow bone)
Taste and Smell Experiment
Result:
|
Onion |
Carrot |
Apple |
Rose-apple |
|
|
Salty |
✔ | ✔ | ||
|
Sweet |
✔ | ✔✔ | ✔ | |
|
Sour |
✔ | ✔ | ✔✔ | |
|
Bitter |
✔✔ | |||
|
Umami |
✔ | |||
|
Overall |
Apple | Onion
Onion |
Apple
Apple |
Apple
Apple |
Blue Color – First Taster (Pat)
Black Color – Second Taster (Mark)
Analysis:
- We have did some mistakes during the experiment. The first mistake was in cutting the foods. Some of the food were cutting into too big pieces, and might because of this, that’s why the tasters could be able to guess some of the food correctly. To avoid this mistake, we should have be more careful in cutting the food and make sure the size of the foods were not too big. Also we should have find a better knife so it’s easier to cut the food into equal size, because the knife we used during the experiment was not sharp and it was hard in cutting.
- The second mistake that we did was that we didn’t hold the nose of the tasters properly, and this might be one of the biggest mistake, because while they are chewing the food, they could smell it, and therefore they could be able to guess the food correctly. This cause us to have to redo the experiment many times. To avoid this thing to happen, we should have hold the nose of the taster more tightly and correctly.
- And the last mistake we did was that we put the foods too close to each other. Therefore some of the taste and smell of the food got mixed up. We should have avoid this by put the groups of food farther to each other.
Conclusion:
- In conclusion, after we have did the experiment, we have learned that we couldn’t identified the food that we eat correctly without the sense of smell helping us. As we can see from the result table, both of our tasters think carrot is onion and rose-apple is apple while they were chewing the food. This is because they judged the food by its taste, not the smell and therefore they guess the food incorrectly. Also, we have learned that we couldn’t identified the food just by its texture. As we can see from the result table, when Mark was chewing the onion, he thought that it was apple because he said that it was smooth and crunchy.
Saliva Experiment
Result:
first test tube : starch, water, benedict solution
second test tube : starch, saliva, water, benedict solution
third test tube : glucose, water, benedict solution
Conclusion:
-
We are doing this experiment to prove that our saliva has an enzyme called amylase which which response for break down glucose.
-
As we can see from the result, the first test tube which is in blue color. It contains starch, water and benedict solution, and its color remain the same. This means there was nothing happen in the first test tube and there is no glucose in it.
-
The second test tube which is the middle one in the picture, it had changed color into orange. This test tube is contain with starch, saliva, water, and benedict solution. But as we can see from the picture, there is glucose at the bottom of the test tube. This prove to us that out saliva has amylase, which cut down the bonds between sugar units. In other words, it break down the glycosidic linkage into monosaccharides.
-
And the third test tube which contains glucose, water, and benedict solution. The color of this test tube had change into light orange color. This is because there is glucose in this test tube.
Difference of spores and seeds
Difference of spores and seeds:
|
Seed |
Spore |
| Made by fertilization of gametes (sex)
Diploid Provides food and water for the new life Have protection on the outside Made by meiosis (asexual) Haploid Does not provide food and water for the new life No protection |
Made by meiosis (asexual)
Haploid Does not provide food and water for the new life No protection |
Presentation Note (Bacteria&Archaea, Protist, Fungi, Animal, Plant)
| Kingdom /Domain | Feature | Evolution | Group (different type) | others |
|
Bacteria & Archaea |
-Archaebacteria & Eubacteria are kingdoms
-Prokaryote: A group of organisms that lack of cell nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelles. Most of them are unicellular.
– Bacteria do not reproduce sexually. They produce asexually.
– 3 main shape of the bacteria: Spirilla, Bacilli, Cocci.
-Bacteria cells are smaller than human cells. There are at least 10x as many bacteria as human cells in the body
-Plasmid are circular rings of DNA. Plasmids can be shared from one bacteria to another for survival.
– Binary Fission: form of asexual reproduction without having to breed with the opposite sex.
-Binary Fission: 1.Single DNA molecule replicating > 2.both copies attaching to the cell membrane> 3.cell membrane begins to grow between the 2 DNA molecules> 4.cell membrane pinch inward> 5.cell wall forms between 2 DNA molecule> 6.dividing the cell into 2 daughter cells.
-Archaea are classified in the same way (cocci, spirilla, bacilli)
-Archaeans are organism thats exist in extreme climates and temperatures.
-Archaeas commonly found near volcanic hot springs, acid mine drainage,etc. Some also live in soils, oceans, marshlands, and even human colons.
-Archaea to do both Autotrophs and Heterotrophs.
-Archaea: Ways of Reproduction 1.Binary Fission 2.Fragmentation (small piece breaks off and becomes new cell) 3.Budding (grows out and falls off)
-multiple fission (similar to binary fission but creates around 4 instead of 2 |
-The first prokaryote were chemoautotrophic (getting their energy from simple chemical reaction), Autotrophic came afterwards
|
-Archaebacteria & Eubacteria
-Autotrophic (organism that can make it own food, taking something inorganic and turn to food e.g. photosynthesis) *Photoautotrophic (cyanobacteria) *Chemoautotrophic bacteria
–Heterotrophic (organism that get energy from other living organisms) *Symbiotic (relationship) – neutral: good-good parasite: good-bad *Parasitic *Chemoheterotrophic
-Pathogenic(bacteria that causes disease)
-conditionally pathogenic *intracellular by location (When bacteria are only dangerous when they are transported from one part of the body to another) -Gram stain: *Gram positive-have a thick layer of shell that the stain can penetrate. Darker color, stain goes directly so it changes color
*Gram negative-has an outer membrane covering a thin layer of shell on the outside, (doesn’t let something in that’s why the cell wall doesn’t change color) stain falls off.
-Extremists: Haphile (salt), thermophiles (cold)
|
-Bacteria and archaea are domains
– 190 genes need to keep human alive.
-Bacteria in food: yogurt, cheese, sour milk,etc.
-Good bacteria called probiotics can make healthy people even more healthy, or improve the health of people with intestinal disorders.
-Lactosyntorence people can drink fermented milk since the bacteria broke down the sugar in it
-Lactic acid bacteria are able to kill Listeria.
-Healthy individuals have a diversity of bacteria
-Bactericides fragile help the immune system
-Sabacious oil on our skin protects the bacteria.
-Plasmids can be used for genetic engineering |
| Protist
|
– An organism that lack definite feature a plant, animal, fungi.
– Eukaryote, unicellular, but sometime come together in colonies and act like multicellular.
– Animal like protist: heterotrophic (get food from other living things). *Always unicellular, mobile, eats by surrounding and engulfing their prey, *classify by the way their move (ciliate, pseudopod, sporozoa)
-Plant like protist: Autotrophs. Can move from place to place. Unicellular some are multicellular. They do not have cellular cell wall so they are not plants. Algae is one of the type
-Euglenoids: has a flagella. Does photosynthesis. Has ability to change from autotrophic and heterotrophic to maintain the oxygen level.
– Dinoflagellates: unicellular. Have more than 2 flagella. Found in fresh water. And reproduce asexually.
– Diatoms: (look like a tiny diamond in microscope) unique double shells that are made of silica. Which has 2 types: radial symmetry (rotate smth and look the same) bilateral symmetry (divide something down in the middle)
– Fungi-like protist: all motile at one point (sperm). External digestion. Heterotrophic. 2 group-Water molds and Slime molds. They don’t have cell wall made of chitin, and not multicellular that’s why they are not fungi.
-Algae : can be both unicellular(few times) and multicellular(usually). Live in both fresh and saltwater. 3 type (red algae, green algae, glaucophyte-brown ) |
– Protist evolved from bacteria: membrane folding in to create the nuclear envelope> then went through endosymbiosis (chloroplast and mitochondria)>to become eukaryotic
|
-Classified by the way they move:
*Sarcodina ( move and eat by pseudopods (fake foot which forms when cytoplasm pushes into the cell membrane)
*Ciliate: tiny hairlike structure that help the organism move or sweep food into them. Great at maneuvering and that makes them ferocious hunter. E.G. Paramecium swim in their food, their ciliates push the food around and into their oral groove
*flagellate: a long thin hair-like that whips around to move. A protist can use up to eight flagella at a time.
– Sporozoa: key feature is parasitic. Can move in any of the 3 ways. E.G. Plasmodium which is a genus name, causes malaria.
– water mold: originally classified as fungi(close relative with brown algae and diatoms,) but were closer to water molds. Has diploid cells.
– Slime mold: live in moist places. Decaying plants and trees. Engulf bacteria and other organic material. Can be single celled organism and can join together and become multicellular. 2 types- Cellular and Plasmodial, difference in reproduction which is cellular and unicellular.
|
-Both Cilia and Flagella evolves in the bacteria.
-The only way that a person can get malaria is if the mosquito that carries the malaria blood bites them. Mosquitos and humans are host for malaria.
-When mosquitos bites human. They inject saliva (sporozoites-inside it). The sporozoites stage goes into the liver, inside the liver in became the merozoites which then injects the blood. *gamete: sperm and eggs. Mosquitoes drink the blood, sperm and eggs combined in the mosquitoes but it’s made in human.
– animal and fungi are the most close cuz they
-opisthokont: imaginary group of fungi and animal.
Ways to reproduce: unicellular and multicellular.
– Important to human: *human benefit from the gas that protist produce (oxygen). *protist also help to recycle important chemicals such as nitrogen, carbon, etc. *responsible for decomposing and recycling nutrient.
-bioremediation (using living thing to fix dirt.) bacteria and protist are the main ones doing this. |
| Fungi | -Eukaryotic
-Achlorphyllous (no chlorophyll – no photosynthesis)
-Unicellular (some like yeast) -Multicellular (Most)
-Membrane-bound organelles
-Cell wall composed of polysaccharide and chitin
-Reproduce sexually or asexually
-Hyphae is like the root of a fungi, they absorb nutrients and water and as well sexual reproduction
-Mycelium is a network of hyphae. Bunch of hyphae together.
-Spores are cells that are covered by a thick cell wall
-Fungi cell wall contains chitin: it strengthens the cells of fungi
|
-Fungi and animal (most relative) came from protest and they belong to Opisthokont.
-Mycorrhizae: first living thing on land, which are fungi and plant living together and plant growth. The combination of fungi and plant.
|
-Zoospores: spores that are like animals because they have tails and can move.
-Phyla of Fungi: Chytridionyta: (also called imperfect fungi because scientist never saw them have sex) produce sexually and asexually but we never saw it (e.g. yeast) Lives mostly in water. They use zoospores to asexually produce. Gametothallas
Zygomycota: mold and decomposing fungi, produce sexually by using the zygospore.
Ascomycota- Looks like a sac or a cup, spores are produced inside the sac or ascus. Produce by using ascospore. Sac fungi are decomposers.
Basidiomycota- Basidium is the reproductive organ which makes the spores. Spores are called basidious spores.
-Mycota means fungus
-Imperfect fungi join together to become layers and they can produce cheese and some are parasite.
-lichens are protist or photosynthetic bacteria living with a fungus. Both sexual and asexual, Protist does photosynthesis and the fungus provides protection. It breaks down rocks and helps make the soil.
-Yeast are unicellular. They reproduce by budding.
|
-decomposers
-mycelium: important because they release enzyme into their surrounding and break down food for other organism as well as anchoring the soil (holds the soil down as it grows across the surface), recycling
-fungi break down poop into oxygen, hydrogen and carbon for plants to absorb
-food
-plasmogamy: cells grow together and join together (into each other). 1 cell 2 nuclei.
Karyogamy: double number of chromosomes because of 2 nuclei
-decompose and recycle
-Some fungi are used to make antibiotics, fungi use it to stop bacteria from taking all their food
-causes diseases such as the athlete foot (itchy)
|
| Animal | -motility
-multicellular -heterotrophs -diploidy -reproduction -eukaryote -no cell walls
-body symmetry: bilateral, radial |
-opisthokont: term to show a division of fungi and animal.
– protist plant opisthokont fungi animal
-flat worm: acoelomate (no space)
-round worm: pseudocoelamate (space outside of endoderm)
-worm: coelomate (some space and connect as well) |
-coelams: worms (flat worm, round worm-fake or pserdo)
-Protostomes: gastostorm make mouth.
-Deuterostomes: gastostorm make anus.
-Archeneteron: becomes the stomach or gastrovascular.
-Spiral cleavage: go around (circle)
-radio cleavage: in bands
-Porifera: sponges, no true-tissue, no symmetry.
– Cnidarian: true-tissue, radial symmetry, (jelly-fish)
-platyhelminthes: flat worm.
-Rotidera
-Nematoda: round worm
– Mollusca: small, squid, octopus.
-Annalida
-Artheropod: most successful animal because exoskeleton, chitin cell wall.
-Chordata |
– opisthokont: reproduction – starts from the haploid sperm or egg. Then they fertilize.
-Somatic cells: non-sex cells -Germ cells: sex cell if they do mitosis then it is a alteration of generation.
-The formation of blastula and gastrula: fertilization into zygote.
-Blastula: hollow ball of cell made by cleavage of the zygote.
–Gastrulation: make your mouth or anus or both.
-Invagination: push something in.
-2 layered animal: diploblastic. 3 layered animal: triploblastic. — ectoderm(skin)m nesoderm, endoderm(inside skin)
-EXCEPT SPONGES: sponge doesn’t goes to blastula stage.
-cell specialize tissue: one job. (e.g. Muscle cell)
-Tissue: cells working together of the same function.
-Relevant to us: we are animal, eat for food, pet, labor.
|
| Plant | -Do photosynthesis
–Eukaryotes
-Multicellular
-Cellulose cell wall
-Indeterminate, open growth
-Cuticles- allows plants to live on land
-Reproduce sexually chlorophyll
|
-Ancestor are protest.
-One of the closest to green algae.
-Don’t have cell wall. |
–Vascular plants:
-Vascular bundle -Roots absorb stuff Can stand straight (xylem) -Vascular tissue includes xylem and phloem -Phloem moves sugar. -Xylem is moving water up.
–Non-vascular plants: -No vascular bundle -Small -Depend on osmosis and diffusion -Need water for reproduction. –Flowers are reproductive parts of plants. –Gymnosperms: -Ex: cedars -No fruit, cones -Adapted to dry climate -Needle like leave -Thick cuticle -Depend on pollination of seed. -Angiosperms: -Ex: crab apple -Flowers and fruits are reproductive structures. -Have a fruit. -Nutrition for the seed. -Get seed dispersal. -Monocots: -Ex: corn -1 left, cotyledon -Vascular bundle is scaltered. -Germinate with one baby leaf or cotyledon. -Venation is parallel. -Peddles are in multiples of three. -Dicots: -EX: magnolia flower -Venation is net like -Ring like vascular bundle -Two cotyledons -Has veins that are brunch together. -Vascular bundle is gathered. -Peddles are in multiples of 4 or 5.
|
–Plant cuticle:
-Protective layer of a green aerial parts of a land plant. -Helps prevent uncontrolled water loss and solutes, and ingression from pests and pathogen.
-It is a waxy layer on the surface of the leafs and protect against pathogen and transportation. -Alternation of generation: -Life cycle with both haploid and diploid parts. -Alternation of generation (moss): -Gametophytes makes gametes. The haploid part is more important. Only non-vascular plant. archegonoum female sex part. Antherididm male part of a moss and fern. -Alternation of generation (fern): -Different lives in complete separate life. Prothallamus- gametophyte of the fern. -Frond- is the sporophyte. Evolve from gametophyte become more important to equal. -Seed dispersal: -Moving the seeds around. -Wind, bursting, shakers, water, animal food, drop and roll, catching a lift. –Pollination: -Pollon -Cross pollination: one flower pollinating the other. -Self pollination: pollinating of yourself. -Archegonium (the female reproductive structure) -Antheridium (the male reproductive structure) –Moss Life Cycle -start from where there is a zygote (a fertilized egg cell) inside gametophyte. -mitosis happens and zygote becomes a sporophyte. -the sporophyte grows into a long thing with a capsule at the top of it. -it grows out of the gametophyte. -then meiosis happens. It produces spores..which are haploid. -when the capsule becomes matured, the capsule breaks and the spores go with the wind and spread. -the spores frow into gametophyte. -gametophytes make eggs and sperms. -the sperm swims to an egg and fertilize. -it creates a zygote and thats were we started. |